Learn the psychology behind habit-forming SaaS products. Reduce churn by 40% using behavioral triggers, variable rewards, and user investment strategies proven by top companies.

Why 90% of SaaS Users Abandon Products After Free Trials
Every SaaS founder faces the same nightmare: users sign up, try your product, then vanish after the trial period. Despite competitive features and fair pricing, SaaS churn rates average 5–7% monthly across the industry.
The problem isn’t your features — it’s user psychology. Most SaaS tools never become part of someone’s daily workflow, making them forgettable and replaceable.
In this guide, you’ll learn:
- The 4-step psychology framework used by Slack, Notion, and other sticky SaaS products
- How to reduce SaaS churn by up to 40% using behavioral triggers
- Proven user engagement strategies that create product addiction (ethically)
- Metrics that predict long-term user retention better than DAU/MAU
The Science Behind SaaS Product Addiction
Understanding Dopamine-Driven User Behavior
Your brain releases dopamine not just when good things happen, but when you think they might happen. This is why you compulsively check your phone — anticipation creates stronger engagement than satisfaction.
Key Insight: Predictable rewards lose their power. Variable rewards create lasting engagement.
Most SaaS products fail because they provide consistent, predictable value without leveraging the psychological mechanisms that drive habit formation.
Example: Email notifications are predictable (you know what to expect). Instagram offers variable rewards (sometimes vacation photos, sometimes breaking news). This unpredictability drives compulsive checking.
Press enter or click to view image in full size
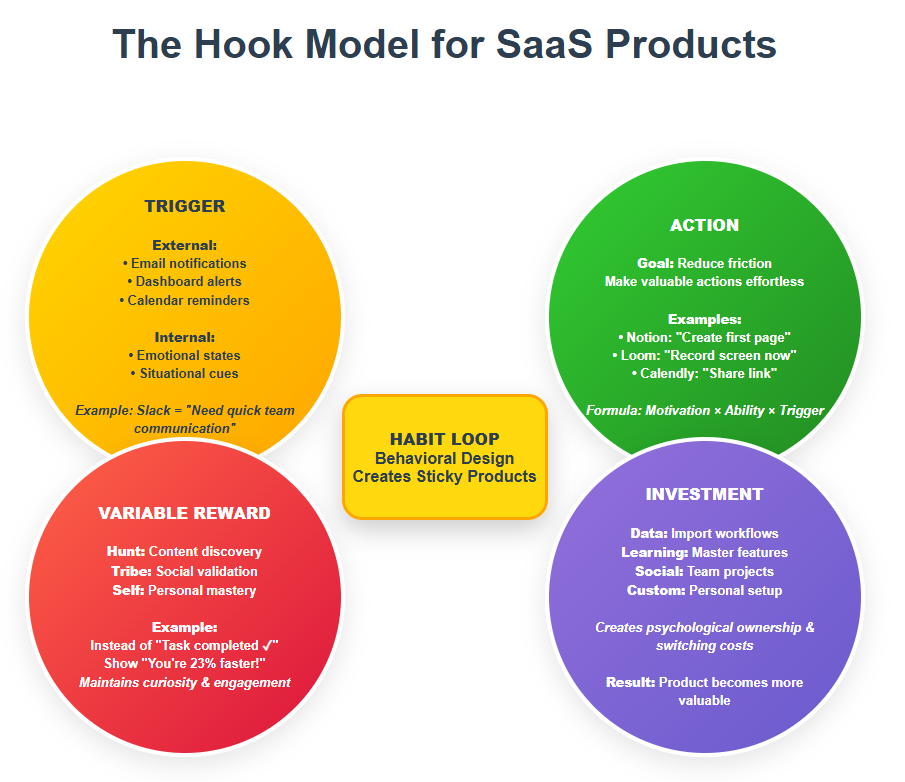
The Hook Model: 4 Steps to Habit-Forming SaaS Products
Based on Nir Eyal’s research in “Hooked,” all sticky products follow this behavioral loop:
1. Trigger: Creating User Activation Points
External Triggers (what you control):
- Email notifications about team activity or project deadlines
- Dashboard alerts highlighting important metrics or anomalies
- Calendar reminders for scheduled tasks or meetings
- Social triggers like mentions, comments, or collaboration requests
Internal Triggers (the holy grail):
- Emotional states that automatically make users think of your product
- Situational cues that prompt immediate usage
SaaS Internal Trigger Examples:
- Uncertainty → Analytics platforms (Google Analytics, Mixpanel)
- Team chaos → Project management tools (Asana, Monday.com)
- Communication friction → Collaboration platforms (Slack, Discord)
- Manual inefficiency → Automation software (Zapier, Make)
Case Study: Slack didn’t just replace email — it became the automatic response to “I need to communicate with my team quickly.” The internal trigger of needing immediate collaboration now defaults to opening Slack for millions of users.
2. Action: Reducing Friction in User Onboarding
A trigger without easy action is worthless. Users must complete desired behaviors with minimal cognitive load and maximum speed to value.
Traditional SaaS Onboarding Problems:
- Lengthy setup processes that delay value realization
- Extensive configuration requirements before first use
- Feature tours that overwhelm instead of activate
Hook Model Approach: Identify the single most valuable action a user can take and make it effortless.
Friction-Reduced Action Examples:
- Notion: “Create your first page” (one click → immediate value)
- Loom: “Record your screen now” (zero setup required)
- Calendly: “Share your scheduling link” (instant utility)
- Canva: “Choose a template” (design in 30 seconds)
Behavioral Formula: Behavior = Motivation × Ability × Trigger
When ability is high (easy to do) and motivation exists, even weak triggers prompt action.
3. Variable Reward: The Psychology of Unpredictable Value
Instead of predictable responses, habit-forming SaaS products introduce beneficial variability that maintains user curiosity and engagement.
Three Categories of SaaS Variable Rewards:
A) Rewards of the Hunt (Content Discovery):
- Personalized insights that change based on user data
- Dynamic recommendations surfacing relevant information
- Unexpected feature suggestions or productivity tips
- Algorithm-driven content that surprises users
B) Rewards of the Tribe (Social Validation):
- Team performance comparisons and achievements
- Peer recognition and collaboration notifications
- Community contributions and user-generated feedback
- Leaderboards and social proof elements
C) Rewards of the Self (Personal Mastery):
- Progress tracking with unexpected milestones
- Skill development pathways revealing surprise unlocks
- Customization options that expand over time
- Achievement systems that celebrate user growth
Implementation Example: Instead of always showing “Task completed ✓”, rotate between:
- Productivity insights: “You’re 23% faster this week!”
- Team updates: “Sarah completed her project early”
- Personal achievements: “You’ve mastered time-blocking”
- Surprise rewards: “You’ve unlocked advanced templates”
4. Investment: Building Psychological Ownership
When users invest time, effort, or data into your product, they develop psychological ownership that creates powerful switching costs.
Effective SaaS Investment Mechanisms:
Data Investment:
- Importing existing workflows and historical information
- Creating custom fields, tags, and organizational systems
- Uploading files, documents, and proprietary content
Learning Investment:
- Mastering advanced features and keyboard shortcuts
- Building expertise with your specific tool and methodology
- Completing certification programs or training modules
Social Investment:
- Inviting colleagues and building shared team projects
- Creating collaborative workspaces and shared resources
- Establishing team dependencies and workflow integrations
Customization Investment:
- Personalizing interfaces, dashboards, and user preferences
- Creating templates, automations, and reusable components
- Setting up integrations with existing software stack
Each investment makes your product more valuable to individual users while making alternatives less attractive — creating compound switching costs.
SaaS User Retention Metrics That Actually Matter
Traditional SaaS metrics like Monthly Active Users (MAU) or feature usage don’t capture habit formation. Track these behavioral indicators instead:
Frequency Indicators:
- Habit Path Analysis: Which user actions predict 12-month retention?
- Trigger Effectiveness: Response time to email notifications and in-app prompts
- Unprompted Usage: Sessions initiated without external triggers
Investment Tracking:
- Profile Completion Rates: Percentage of users completing setup steps
- Social Integration: Users who invite colleagues within first 30 days
- Customization Depth: Average number of personalization actions per user
Retention Cohorts:
- Habit Formation Timeline: Days until usage becomes automatic (typically 21–66 days)
- Investment Correlation: Does deeper investment predict lower churn? (Usually yes)
- Trigger Transition: When users shift from external to internal triggers
Ethical SaaS Psychology: The Manipulation Matrix
With psychological power comes responsibility. Use the Manipulation Matrix to ensure ethical product development:
Ask yourself:
- Would I use this product myself daily?
- Does it materially improve users’ professional lives?
- Are users measurably better off forming this habit?
- Am I solving real problems or creating artificial dependency?
Positive Examples:
- Grammarly: Improves writing skills over time
- Calendly: Reduces scheduling friction permanently
- Notion: Enhances organizational capabilities
Red Flags:
- Features that consume time without providing value
- Notifications designed to interrupt rather than assist
- Artificial scarcity or FOMO tactics
SaaS Psychology Case Studies: What Works in 2025
Slack: Mastering Internal Triggers
Psychology Used: Social validation + immediate communication Result: 10+ million daily active users with 90%+ retention Key Insight: Made team communication friction so low that alternatives feel painful
Notion: Investment-Driven Retention
Psychology Used: Customization investment + personal mastery Result: 30+ million users with high switching costs Key Insight: Users invest dozens of hours customizing workspaces, making migration extremely difficult
Linear: Variable Rewards in B2B
Psychology Used: Beautiful interface + unpredictable insights Result: 20x faster adoption than traditional project management tools Key Insight: Even B2B software can use variable rewards through data visualization and team achievements
Your SaaS Psychology Audit: Implementation Framework
Current State Analysis:
- Trigger Audit: What external triggers are you using? How can you identify internal triggers?
- Action Analysis: What’s your primary user action? Where can you reduce friction?
- Reward Assessment: How predictable are your user rewards? Where can you add beneficial variability?
- Investment Review: What investments do users make? How can you increase commitment?
Optimization Opportunities:
- A/B test different trigger strategies (email timing, notification copy, in-app prompts)
- Measure action completion rates across user segments and onboarding flows
- Experiment with reward variability in notifications, achievements, and user feedback
- Track correlation between investment depth and retention using cohort analysis
Frequently Asked Questions About SaaS User Psychology
Q: How long does it take to form a SaaS habit? A: Research shows 21–66 days for simple habits, but SaaS products typically see habit formation within 30–45 days of consistent use.
Q: Can B2B SaaS products use psychology tactics ethically? A: Absolutely. Focus on reducing professional friction, improving productivity, and creating genuine workflow value rather than time-wasting engagement.
Q: What’s the difference between habit-forming and addictive products? A: Habit-forming products improve users’ lives and productivity. Addictive products consume time without providing proportional value.
Q: How do you measure psychological engagement in SaaS? A: Track unprompted usage, investment behaviors, and trigger-to-action response times rather than just session duration or feature clicks.
Q: Which SaaS categories benefit most from behavioral design? A: Productivity tools, communication platforms, analytics dashboards, and project management software see the highest impact from psychological optimization.
Next Steps: Building Your Habit-Forming SaaS Product
The SaaS landscape grows more competitive daily. Success no longer depends solely on features or pricing — winners understand human psychology and design products that become positive, habitual parts of users’ professional lives.
Your implementation roadmap:
- Week 1: Complete the Hook Model audit for your current product
- Week 2: Identify and test one internal trigger opportunity
- Week 3: Optimize your highest-friction user action
- Week 4: Implement variable reward testing in notifications or achievements
Start with one element of the Hook Model and measure behavioral impact. Whether redesigning onboarding, introducing variable rewards, or identifying internal triggers, focus on user value over manipulation.
Remember: The goal isn’t mindless addiction — it’s building tools so valuable and seamlessly integrated that users can’t imagine working without them.
helps SaaS companies reduce churn through behavioral design and user psychology. Follow for more insights on product growth, user retention, and ethical engagement strategies.
I help SaaS companies reduce churn by applying behavioral design and user psychology. Follow for practical insights on product growth, user retention, and ethical engagement strategies.

